Wireshark allows you to analyze the traffic inside your network with various tools. If you want to see what’s going on inside your network or have issues with network traffic or page loading, you can use Wireshark. It allows you to capture the traffic, so you can understand what the problem is or send it to support for further assistance. Keep reading this article, and you’ll learn how to capture http traffic in Wireshark.
Installing Wireshark
Installing Wireshark is an easy process. It’s free tool across different platforms, and here is how you can download and install it:
Wireshark Mac Download; Wireshark For Windows 10; Download WireShark for Mac - A free and open-source network protocol protocol analyzer that enables you to capture the network traffic and analyze it in detail. Wireshark is the world's foremost network protocol analyzer, and is the de facto (and often de jure) standard across many industries. Wireshark For Mac free download - Wireshark (64-bit), WinZip Mac, Technitium MAC Address Changer, and many more programs. Download TCP Dump. In my view, this the best alternative for Wireshark which helps to analyze and view packet captures taken on the dashboard. Right after installing Cloudshark on your Mac or window, you will have the option to output your packet captures to the tool. If you need a rollback of Wireshark, check out the app's version history on Uptodown. It includes all the file versions available to download off Uptodown for that app. Download rollbacks of Wireshark for Mac. Any version of Wireshark distributed on Uptodown is completely virus-free and free to download at no cost. 3.5.0 Aug 31rd, 2021.
Windows & Mac Users
- Open your browser.
- Visit https://www.wireshark.org/download.html.
- Select the version for your device.
- Wireshark will be downloaded to your device.
- Install it by following the instructions in the package.
Linux Users
If you’re a Linux user, you can find Wireshark in the Ubuntu Software Center. Download it from there and install it according to the instructions in the package.
Capturing HTTP Traffic in Wireshark
Now that you’ve installed Wireshark on your computer, we can move on to capturing http traffic. Here are the steps to do it:
- Open your browser – You can use any browser.
- Clear cache – Before capturing the traffic, you need to clear your browser’s cache. You can do this if you go to your browser’s settings.
- Open Wireshark.
- Tap “Capture.”
- Tap “Interfaces.” You will now see a pop-up window on your screen.
- Choose the interface. You probably want to analyze the traffic going through your ethernet driver.
- Once you’ve selected the interface, tap “Start” or tap “Ctrl + E.”
- Now go back to your browser and visit the URL you want to capture traffic from.
- Once you’re done, stop capturing traffic. Go back to Wireshark and tap “Ctrl + E.”
- Save the captured traffic. If you have network issues and want to send the captured traffic to support, save it into a *.pcap format file.
Capturing Packets in Wireshark
Besides capturing http traffic, you can capture whatever network data you need in Wireshark. Here is how you can do this:
- Open Wireshark.
- You’ll see a list of available network connections you can examine. Select the one you’re interested in. If you want, you can analyze multiple network connections at once by pressing “Shift + Left-click.”
- Now you can start capturing packets. You can do this in several ways: The first one is by tapping the shark fin icon at the top-left corner. The second one is tapping “Capture” and then tapping “Start.” The third way to start capturing is by tapping “Ctrl + E.”
While capturing, Wireshark will display all the captured packets in real-time. Once you’re done capturing packets, you can use the same buttons/shortcuts to stop capturing.
Wireshark Filters
One of the reasons Wireshark is one of the most famous protocol analyzers today is its ability to apply various filters to the captured packets. Wireshark filters can be divided into capture and display filters.
Capture Filters
These filters are applied before capturing data. If Wireshark captures data that doesn’t match the filters, it won’t save them, and you won’t see them. So, if you know what you’re looking for, you can use capture filters to narrow down your search.
Here are some of the most used capture filters you can use:
- host 192.168.1.2 – Capture all traffic associated with 192.168.1.2.
- port 443 – Capture all traffic associated with port 443.
- port not 53 – Capture all traffic except the one associated with port 53.
Display Filters
Depending on what you’re analyzing, your captured packets may be very hard to go through. If you know what you’re looking for, or if you want to narrow down your search and exclude the data you don’t need, you can use display filters.
Here are some of the display filters you can use:
- http – If you’ve captured a number of different packets, but you want to see only the http-based traffic, you can apply this display filter, and Wireshark will show you only those packets.
- http.response.code 404 – If you’re having trouble loading certain web pages, this filter might be useful. If you apply it, Wireshark will only show the packets where “404: Page not found” was a response.
It’s important to note the difference between capture and display filters. As you’ve seen, you apply capture filters before, and display filters after capturing packets. With capture filters, you discard all packets that don’t fit the filters. With display filters, you don’t discard any packets. You just hide them from the list in Wireshark.
Additional Wireshark Features
Although capturing and filtering packets is what makes Wireshark famous, it also offers different options that can make your filtering and troubleshooting easier, especially if you’re new at this.
Colorization Option
You can color packets in the Packet List according to different display filters. This allows you to emphasize the packets you want to analyze.
There are two types of coloring rules: temporary and permanent. Temporary rules are applied only until you close the program, and permanent rules are saved until you change them back.
You can download sample coloring rules here, or you can create your own.
Promiscuous Mode
Wireshark captures traffic coming to or from the device where it’s running. By enabling the promiscuous mode, you’re able to capture the majority of traffic on your LAN.
Command Line
If you’re running your system without a GUI (Graphic user interface), you can use Wireshark’s Command Line Interface. You can capture packets and review them on a GUI.
Statistics
Wireshark offers a “Statistics” menu you can use to analyze captured packets. For example, you can view file properties, analyze traffic between two IP addresses, etc.
FAQs
How do I read the data captured in WireShark?
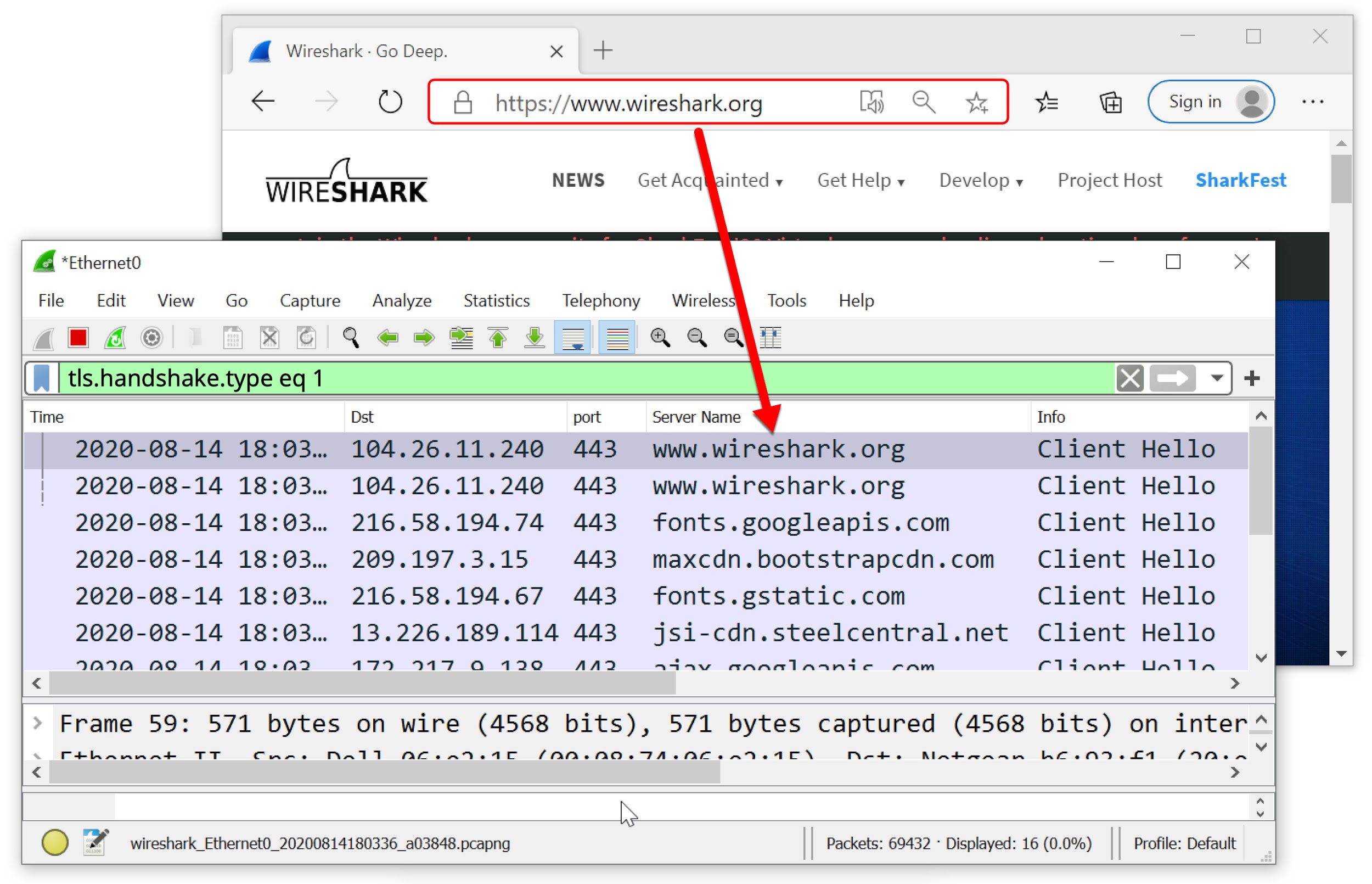
Once you’re done capturing packets, Wireshark will show all of them in a packet list pane. If you want to focus on a specific capture, double-click on it, and you can read more information about it.
You can decide to open a particular capture in a separate window for easier analysis:
1. Choose the packet you want to read.
2. Right-click on it.
3. Tap “View.”
4. Tap “Show Packet in New Window.”
Here are some details from the packet list pane that will help you with reading captures:
1. No. – The number of a captured packet.
2. Time – This shows you when the packet was captured with regards to when you started capturing. You can customize and adjust the value in the “Settings” menu.
3. Source – This is the origin of a captured packet in the form of an address.
4. Destination – The destination address of a captured packet.
5. Protocol – The type of a captured packet.
6. Length – This shows you the length of a captured packet. This is expressed in bytes.
7. Info – Additional information about a captured packet. The type of information you see here depends on the type of the captured packet.
All of the above columns can be narrowed down with the use of display filters. Depending on what you’re interested in, you can interpret Wireshark captures easier and faster by applying different filters.
In a World of Fish, Be a Wireshark
Now you’ve learned how to capture http traffic in Wireshark, along with useful information about the program. If you want to inspect your network, troubleshoot issues, or ensure everything’s in order, Wireshark is the right tool for you. It’s easy to use and interpret, and it’s free.
Have you used Wireshark before? Tell us in the comment section below.
Table of Contents
Quicklinks: Wireshark: Installation Chapter
Install Wireshark with a Package Manager
Where available, prefer your package manager. Note that Wireshark v3 is not currently available on many Linux package managers (this will change soon).
| System | Install Command | Latest Version |
|---|---|---|
| Linux | $PkgManager install wireshark | 2.6.8 and below |
| Macos | brew install --cask wireshark | 3.0.2 |
| Windows | choco install wireshark | 3.0.2 |
Installing tshark Only
Note: If you have not used tshark before, you should install the wiresharkpackage as above before limiting yourself to the CLI.
If you want to install just tshark and no Qt/GUI components, this is possible onvarious linux distributions. The package is called tshark or wireshark-clidepending on the platform.
Install the package tshark:
- Alpine >= 3.9
- Debian >= 9
- FreeBSD >= 11
- OpenMandriva >= 3.0
- PCLinuxOS
- Ubuntu >= 14.04
Install the package wireshark-cli.
- Arch Linux
- CentOS >= 8
- Fedora >= 30
- RedHat
For up-to-date package information, check the package registry fortshark andwireshark-cli
Install with a package
To get the most up-to-date official packages, visit Wireshark’s Download Page.
There are multiple packages available from Wireshark’s download page. The installation is simple, but make sure to check the components that.
Install from Source

Linux currently does not have packages in official repositories, so if you want the latest, you have to build it (this will likely change soon).
Linux, v3.0.0
You need to install from source to get v3 on Linux. This will get a clean system on Ubuntu18.04 to an install:
If you are on a different system, only the last 3 steps apply. Make sure thatyou’ve satisfied the other dependencies. cmake will kindly let you know if youhaven’t.
Check Installation
1. Check Version
If the version doesn’t match the expected one, you may want toinstall from source or use Wireshark’s download page.
2. Check Interfaces
tshark -D will list all interfaces that it sees.
dumpcap does not see and cannot capture on virtual interfaces. This means that dumpcap -D will show fewer interfaces than tshark -D.
Different systems will report different interfaces. tshark will treat the first interface as the default interface and capture from it by default.In other words, tshark aliases to tshark -i 1. You may need to use sudo depending on your installation.Default interfaces on installs of macos, windows, linux, and freebsd are shown below.
3. Test Live Capture
Entering the tshark command should immediately start capturing packets on the default interface. If you donot see packets, check out Choosing an Interface.
4. Make Sure Utilities are on $PATH
Setting up your environment should be done once and done well. There are a coupleAdditional work is usually necessary to make sure all utilities are on the path.
bash
You can verify whether all are installed with the following:
If a util is installed but not on your $PATH, you can use find / -name $util 2>/dev/nullto find out where it may be. For example, on Linux for 3.0.0, extcap tools areat /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/wireshark/extcap. To add them to your path, useecho 'export PATH=$PATH:$folder' >> ~/.profile.
Powershell on Windows
Currently, extcap utils need to bemoved from Wiresharkextcap => Wiresharkto be useable. If you have not added your %Program Files% to your $PATH, you cando that with an Admin user:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('PATH', '$PATH;$ENV:ProgramFilesWireshark', 'Machine')
How To Download Wireshark Mac Download
You will need to reopen Powershell for the $PATH to be updated.



